{dataClass}
Dataclass names can be used directly in the REST requests to work with entities, entity selections, or methods of the dataclass.
Available syntaxes
| Syntax | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| {dataClass} | /Employee | Returns all the data (by default the first 100 entities) for the dataclass |
| {dataClass}({key}) | /Employee(22) | Returns the data for the specific entity defined by the dataclass's primary key |
| {dataClass}:{attribute}(value) | /Employee:firstName(John) | Returns the data for one entity in which the attribute's value is defined |
| {dataClass}/{method} | /Employee/getHighSalaries | Executes a project method and returns an object or a collection (the project method must be exposed) |
| {dataClass}({key})/{method} | /Employee(22)/getAge | Returns a value based on an entity method |
{dataClass}
Returns all the data (by default the first 100 entities) for a specific dataclass (e.g., Company)
Description
When you call this parameter in your REST request, the first 100 entities are returned unless you have specified a value using $top/$limit.
Here is a description of the data returned:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __entityModel | Text | Name of the dataclass. |
| __COUNT | Number | Number of entities in the dataclass. |
| __SENT | Number | Number of entities sent by the REST request. This number can be the total number of entities if it is less than the value defined by $top/$limit. |
| __FIRST | Number | Entity number that the selection starts at. Either 0 by default or the value defined by $skip. |
| __ENTITIES | Collection | This collection of objects contains an object for each entity with all its attributes. All relational attributes are returned as objects with a URI to obtain information regarding the parent. |
Each entity contains the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __KEY | Text | Value of the primary key defined for the dataclass. |
| __TIMESTAMP | Date | Timestamp of the last modification of the entity |
| __STAMP | Number | Internal stamp that is needed when you modify any of the values in the entity when using $method=update. |
If you want to specify which attributes you want to return, define them using the following syntax {attribute1, attribute2, ...}. For example:
GET /rest/Company/name,address
Example
Return all the data for a specific dataclass.
GET /rest/Company
Result:
{
"__entityModel": "Company",
"__GlobalStamp": 51,
"__COUNT": 250,
"__SENT": 100,
"__FIRST": 0,
"__ENTITIES": [
{
"__KEY": "1",
"__TIMESTAMP": "2020-04-10T10:44:49.927Z",
"__STAMP": 1,
"ID": 1,
"name": "Adobe",
"address": null,
"city": "San Jose",
"country": "USA",
"revenues": 500000,
"staff": {
"__deferred": {
"uri": "http://127.0.0.1:8081/rest/Company(1)/staff?$expand=staff"
}
}
},
{
"__KEY": "2",
"__TIMESTAMP": "2018-04-25T14:42:18.351Z",
"__STAMP": 1,
"ID": 2,
"name": "Apple",
"address": null,
"city": "Cupertino",
"country": "USA",
"revenues": 890000,
"staff": {
"__deferred": {
"uri": "http://127.0.0.1:8081/rest/Company(2)/staff?$expand=staff"
}
}
},
{
"__KEY": "3",
"__TIMESTAMP": "2018-04-23T09:03:49.021Z",
"__STAMP": 2,
"ID": 3,
"name": "4D",
"address": null,
"city": "Clichy",
"country": "France",
"revenues": 700000,
"staff": {
"__deferred": {
"uri": "http://127.0.0.1:8081/rest/Company(3)/staff?$expand=staff"
}
}
},
{
"__KEY": "4",
"__TIMESTAMP": "2018-03-28T14:38:07.430Z",
"__STAMP": 1,
"ID": 4,
"name": "Microsoft",
"address": null,
"city": "Seattle",
"country": "USA",
"revenues": 650000,
"staff": {
"__deferred": {
"uri": "http://127.0.0.1:8081/rest/Company(4)/staff?$expand=staff"
}
}
}
.....//more entities here
]
}
{dataClass}({key})
Returns the data for the specific entity defined by the dataclass's primary key, e.g., Company(22) or Company("IT0911AB2200")
Description
By passing the dataclass and a key, you can retrieve all the public information for that entity. The key is the value in the attribute defined as the Primary Key for your dataclass. For more information about defining a primary key, refer to the Modifying the Primary Key section in the Data Model Editor.
If you want to specify which attributes you want to return, define them using the following syntax {attribute1, attribute2, ...}. For example:
GET /rest/Company(1)/name,address
If you want to expand a relation attribute using $expand, you do so by specifying it as shown below:
GET /rest/Company(1)/name,address,staff?$expand=staff
Example
The following request returns all the public data in the Company dataclass whose key is 1.
GET /rest/Company(1)
Result:
{
"__entityModel": "Company",
"__KEY": "1",
"__TIMESTAMP": "2020-04-10T10:44:49.927Z",
"__STAMP": 2,
"ID": 1,
"name": "Apple",
"address": Infinite Loop,
"city": "Cupertino",
"country": "USA",
"url": http://www.apple.com,
"revenues": 500000,
"staff": {
"__deferred": {
"uri": "http://127.0.0.1:8081/rest/Company(1)/staff?$expand=staff"
}
}
}
{dataClass}:{attribute}(value)
Returns the data for one entity in which the attribute's value is defined
Description
By passing the dataClass and an attribute along with a value, you can retrieve all the public information for that entity. The value is a unique value for attribute, but is not the primary key.
GET /rest/Company:companyCode(Acme001)
If you want to specify which attributes you want to return, define them using the following syntax {attribute1, attribute2, ...}. For example:
GET /rest/Company:companyCode(Acme001)/name,address
If you want to use a relation attribute using $attributes, you do so by specifying it as shown below:
GET /rest/Company:companyCode(Acme001)?$attributes=name,address,staff.name
Example
The following request returns all the public data of the employee named "Jones".
GET /rest/Employee:lastname(Jones)
{dataClass}/{method} and {dataClass}({key})/{method}
Returns an object or a collection based on a project method.
Description
Project methods are called through a dataclass (table) or an entity (record), and must return either an object or a collection.
POST /rest/Employee/getHighSalaries
POST /rest/Employee(52)/getFullName
4D Configuration
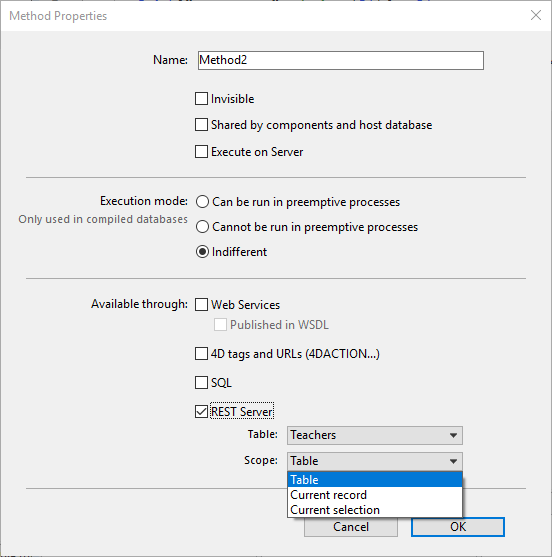
To be called in a REST request, a method must:
- have been declared as "Available through REST server" in 4D,
- have its master table and scope defined accordingly:
- Table: 4D table (i.e. dataclass) on which the method is called. The table must be exposed to REST.
- Scope: This setting is useful when the method uses the 4D classic language and thus, needs to have a database context on the server side.
- Table -for methods applied to the whole table (dataclass)
- Current record -for methods applied to the current record (entity) using the
\{dataClass\}(key)/{method}syntax. - Current selection -for methods applied to the current selection
Passing Parameters to a Method
You can also pass parameters to a method in a POST.
POST /rest/Employee/addEmployee
You can POST data in the body part of the request, for example:
["John","Smith"]
Examples
Table scope
Call of a getAverage method:
- on [Employee] table
- with Table scope
//getAverage
ALL RECORDS([Employee])
$0:=New object("ageAverage";Average([Employee]age))
POST /rest/Employee/getAverage
Result:
{
"result": {
"ageAverage": 44.125
}
}
Current record scope
Call of a getFullName method:
- on [Employee] table
- with Current record scope
//getFullName
$0:=New object("fullName";[Employee]firstname+" "+[Employee]lastname)
POST /rest/Employee(3)/getFullName
Result:
{
"result": {
"fullName": "John Smith"
}
}
Current selection scope
Call of a updateSalary method:
- on [Employee] table
- with Current selection scope
//updateSalary
C_REAL($1;$vCount)
READ WRITE([Employee])
$vCount:=0
FIRST RECORD([Employee])
While (Not(End selection([Employee]))
[Employee]salary:=[Employee]salary * $1
SAVE RECORD([Employee])
$vCount:=$vCount+1
NEXT RECORD([Employee])
End while
UNLOAD RECORD([Employee])
$0:=New object("updates";$vCount)
POST /rest/Employee/updateSalary/?$filter="salary<1500"
POST data (in the request body): [1.5]
Result:
{
"result": {
"updated": 42
}
}