Forms
Forms provide the interface through which information is entered, modified, and printed in a desktop application. Users interact with the data in a database using forms and print reports using forms. Forms can be used to create custom dialog boxes, palettes, or any featured custom window.
Forms can also contain other forms through the following features:
Creating forms
You can add or modify 4D forms using the following elements:
- 4D Developer interface: Create new forms from the File menu or the Explorer window.
- Form Editor: Modify your forms using the Form Editor.
- JSON code: Create and design your forms using JSON and save the form files at the appropriate location. Example:
{
"windowTitle": "Hello World",
"windowMinWidth": 220,
"windowMinHeight": 80,
"method": "HWexample",
"pages": [
null,
{
"objects": {
"text": {
"type": "text",
"text": "Hello World!",
"textAlign": "center",
"left": 50,
"top": 120,
"width": 120,
"height": 80
},
"image": {
"type": "picture",
"pictureFormat": "scaled",
"picture": "/RESOURCES/Images/HW.png",
"alignment":"center",
"left": 70,
"top": 20,
"width":75,
"height":75
},
"button": {
"type": "button",
"text": "OK",
"action": "Cancel",
"left": 60,
"top": 160,
"width": 100,
"height": 20
}
}
}
]
}
Project form and Table form
There are two categories of forms:
-
Project forms - Independent forms that are not attached to any table. They are intended more particularly for creating interface dialog boxes as well as components. Project forms can be used to create interfaces that easily comply with OS standards.
-
Table forms - Attached to specific tables and thus benefit from automatic functions useful for developing applications based on databases. Typically, a table has separate input and output forms.
Typically, you select the form category when you create the form, but you can change it afterwards.
Form pages
Each form has is made of at least two pages:
- a page 1: a main page, displayed by default
- a page 0: a background page, whose contents is displayed on every other page.
You can create multiple pages for an input form. If you have more fields or variables than will fit on one screen, you may want to create additional pages to display them. Multiple pages allow you to do the following:
- Place the most important information on the first page and less important information on other pages.
- Organize each topic on its own page.
- Reduce or eliminate scrolling during data entry by setting the entry order.
- Provide space around the form elements for an attractive screen design.
Multiple pages are a convenience used for input forms only. They are not for printed output. When a multi-page form is printed, only the first page is printed.
There are no restrictions on the number of pages a form can have. The same field can appear any number of times in a form and on as many pages as you want. However, the more pages you have in a form, the longer it will take to display it.
A multi-page form has both a background page and several display pages. Objects that are placed on the background page may be visible on all display pages, but can be selected and edited only on the background page. In multi-page forms, you should put your button palette on the background page. You also need to include one or more objects on the background page that provide page navigation tools for the user.
Fluent UI rendering
Fluent UI support is currently in the Developer Preview phase. It should not be used in production.
On Windows, 4D supports Fluent UI form rendering, Microsoft's modern graphical user interface design, based upon WinUI 3 technology. WinUI 3 is the foundation of the Windows App SDK and represents the upcoming Windows graphical interfaces.
Fluent UI rendering offers modern and attractive controls, support of dark/light system themes, smoother rendering optimized for high-resolution displays, and consistent user experience aligned with recent Microsoft applications.
| Light theme | Dark theme |
|---|---|
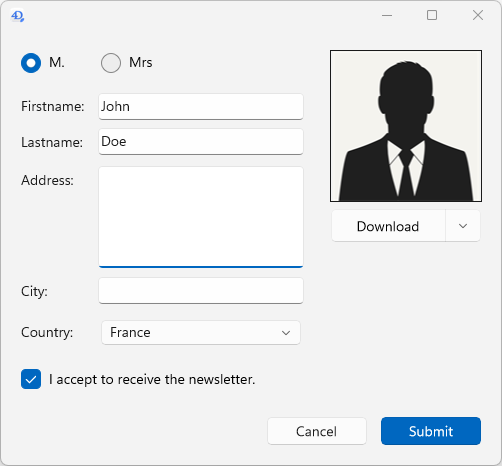 | 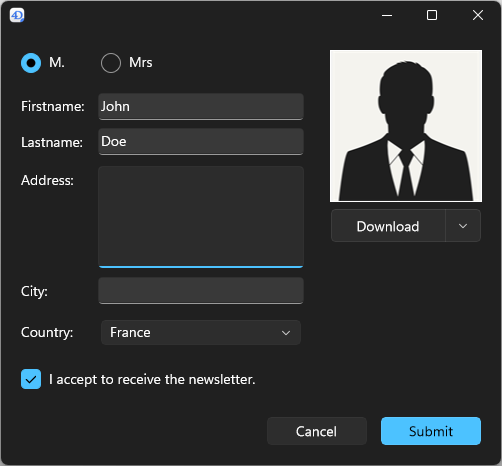 |
This feature can be used in 4D projects on Windows. It is not available on macOS or in binary 4D databases on Windows.
Requirements
The Fluent UI rendering requires that the Windows App SDK be installed on your machine. You need to make sure this SDK is installed on any Windows machine displaying your forms.
If necessary, you can install the Windows App SDK. For convenience, the 4D installer provides a link to download the Windows App SDK installer. You can also visit the Microsoft download page. We recommend using the version provided by the 4D installer, which offers optimal compatibility.
If the Windows App SDK is not properly installed, 4D will render all your forms in classic mode with no error and the following warning will be recorded in the diagnostic log: "Fluent UI is required but not available. The application runs in the Classic Windows look."
Enabling the Fluent UI rendering
You can enable the Fluent UI rendering mode at the application level or at the form level. Form setting has priority over application setting.
Application setting
Check the Use Fluent UI on Windows option in the "Interface" page of the Settings dialog box.
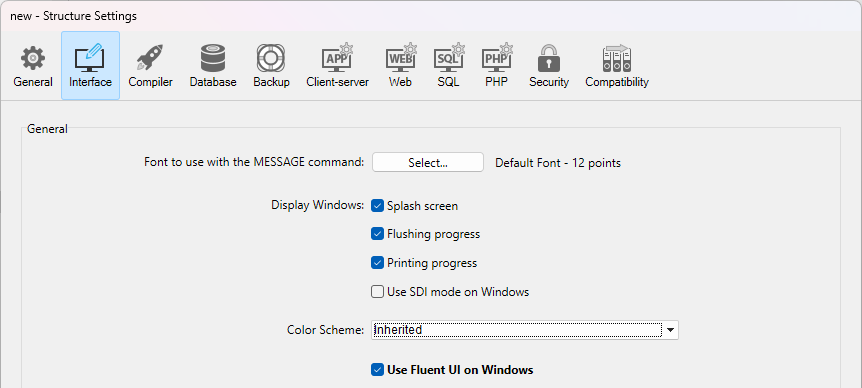
In this case, the Fluent UI rendering mode will be used by default on Windows for all forms.
If the current configuration is not compliant with the Fluent UI requirements, an error message is displayed next to the check box.
Form setting
Each form can define its own rendering via the Widget appearance property. The following options are available:
- Inherited: inherits the global application setting (default),
- Classic: uses the classic Windows style,
- Fluent UI: enables the modern rendering based on Fluent UI.
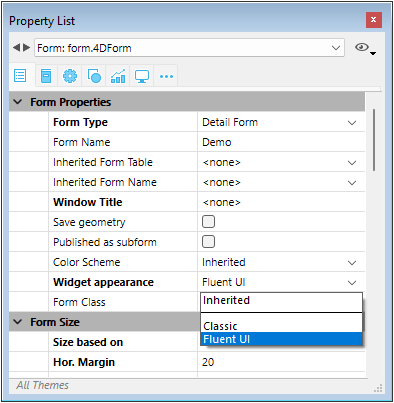
The corresponding JSON form property is fluentUI with value undefined (i.e. inherited, default value), "true" or "false".
CSS
The form-theme CSS media query allows you to configure several styles depending on the used theme.
Specific behaviors
When using 4D forms with Fluent UI rendering, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- The
FORM themecommand returns the actual display theme of the current form. Possible values: "Classic" or "FluentUI". If there is no current form or if the command is called on macOS, and empty string is returned. - The
Application infocommand allows you to know if Fluent UI can be used (canUseFluentUIproperty) or is being used (useFluentUIproperty). - If
GET STYLE SHEET INFOis called in the context of a form, the information returned relates to the current appearance of the form (Classic or FluentUI). If the command is called outside the context of a form, the information returned relates to the global project settings. SET MENU ITEM STYLEwithUnderlineitemStyle parameter is not supported (ignored) for pop up menus.- Stepper form object does not support double-click event.
- Circle buttons are supported (similar as macOS).
- The
WA ZOOM IN/WA ZOOM OUTcommands are not supported in Web areas with system rendering engine. - A focus ring can be added to picture and text inputs.
Inherited Forms
4D forms can use and be used as "inherited forms," meaning that all of the objects from Form A can be used in Form B. In this case, Form B "inherits" the objects from Form A.
References to an inherited form are always active: if an element of an inherited form is modified (button styles, for example), all forms using this element will automatically be modified.
All forms (table forms and project forms) can be designated as an inherited form. However, the elements they contain must be compatible with use in different database tables.
When a form is executed, the objects are loaded and combined in the following order:
- Page zero of the inherited form
- Page 1 of the inherited form
- Page zero of the open form
- Current page of the open form.
This order determines the default entry order of objects in the form.
Only pages 0 and 1 of an inherited form can appear in other forms.
The properties and method of a form are not considered when that form is used as an inherited form. On the other hand, the methods of objects that it contains are called.
To define an inherited form, the Inherited Form Name and Inherited Form Table (for table form) properties must be defined in the form that will inherit something from another form.
A form can inherit from a project form, by setting the Inherited Form Table property to \<None> in the Property List (or " " in JSON).
To stop inheriting a form, select \<None> in the Property List (or " " in JSON) for the Inherited Form Name property.
It is possible to define an inherited form in a form that will eventually be used as an inherited form for a third form. The combining of objects takes place in a recursive manner. 4D detects recursive loops (for example, if form [table1]form1 is defined as the inherited form of [table1]form1, in other words, itself) and interrupts the form chain.
Supported Properties
Associated Menu Bar - Fixed Height - Fixed Width - Form Break - Form Detail - Form Footer - Form Header - Form Name - Form Type - Inherited Form Name - Inherited Form Table - Maximum Height - Maximum Width - Method - Minimum Height - Minimum Width - Pages - Print Settings - Published as Subform - Save Geometry - Window Title