Glossary
Main concepts at a glance
Action
Every action that can be done on a resource. Available actions are: create, read, update, drop, execute, and promote.
Attribute
An attribute is the smallest storage cell in a relational database (see also Relation attribute). Do not confuse dataclass attributes and entity attributes:
- In a dataclass object, each property is a dataclass attribute that maps to a corresponding field in the corresponding table (same name and type).
- In an entity object, entity attributes are properties that contain values for the corresponding datastore attributes.
Attributes and properties are similar concepts. "Attribute" is used to designate dataclass properties that store data, while "property" is more generic and defines a piece of data stored within an object.
AttributePath
An attributePath is the path of an attribute inside a given dataclass or entity. See also PropertyPath.
Class code
Code for the user class function(s).
Computed attribute
A computed attribute doesn't actually store information. Instead, it determines its value based on other values from the same entity or from other entities, attributes or functions. When a computed attribute is referenced, the underlying "computation" is evaluated to determine the value. Computed attributes may even be assigned values where user-defined code determines what to do during the assignment.
Data model class
Extended class available for a data model object.
Data model object
Database objects available through the ORDA concept, i.e. datastore, dataclasses, entities and entity selections.
Data model function
Function of an ORDA data model class.
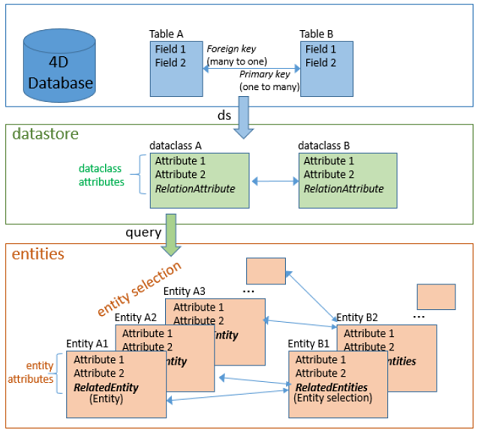
Dataclass
A dataclass is an object model that describes the data. Tables in the database provided by the datastore are handled through dataclasses. Each table in the database provided by the datastore has a corresponding dataclass with the same name. Each field of the table is an attribute of the dataclass.
A dataclass is related to a single datastore.
DataClass class
Class for specific dataclass objects, in which you can add custom functions.
Datastore
A datastore is the interface object provided by ORDA to reference a structure and access its data. The main database, returned by the ds command, is available as a datastore (the main datastore).
A datastore provides:
- a connection to the 4D database
- a set of dataclasses to work with the database
The database can be a 4D local database (the Main datastore), or a 4D Server database exposed as REST resource (a Remote datastore).
A datastore references only a single database. It is, however, possible to open several datastores to access several databases.
DataStore class
Class for datastore objects, in which you can add custom functions.
DataStoreImplementation
Internal name of the generic DataStore class in the 4D class store.
Deep copy
A deep copy duplicates an object and all the references it contains. After a deep copy, a copied collection contains duplicated elements and thus, new references, of all of the orginal elements. See also Shallow copy.
ds
ds is the 4D language command that returns a datastore object reference. It matches the datastore available upon the 4D main database.
Entity
An entity is an object that corresponds to a dataclass model. An entity contains the same attributes as the dataclass.
An entity can be seen as an instance of the dataclass, like a record of the table matching the dataclass in its associated datastore. However, an entity also contains related data. The purpose of the entity is to manage data (create, update, delete).
For more information, see entities.
Entity selection
An entity selection is an object. When querying the datastore, an entity selection is returned. An entity selection is a set of references to entities related to the same dataclass.
An entity selection contains:
- a set of 0 to X entity references,
- a length property (always),
- queryPlan and queryPath properties (if asked while querying).
An entity selection can also be empty.
Generic class
Built-in class for ORDA objects such as entities, or dataclasses. Functions and properties of generic classes are automatically available in user extended classes, e.g. EmployeeEntity.
Lazy loading
Since entities are managed as references, data is loaded only when necessary, i.e. when accessing it in the code or through interface widgets. This optimization principle is called lazy loading.
Main datastore
The Datastore object matching the opened 4D database (standalone or client/server). The main datastore is returned by the ds command.
Method
ORDA objects such as datastores, dataclasses, entity selections, and entities, define classes of objects. They provide specific methods to directly interact with them. These methods are also called member functions. Such methods are used by calling them on an instance of the object.
For example, the query() method is a dataclass member function. If you have stored a dataclass object in the $myClass variable, you can write:
$myClass.query("name = smith")
Mixed data type
In this documentation, "Mixed" data type is used to designate the various type of values that can be stored within dataclass attributes. It includes:
- number
- text
- null
- boolean
- date
- object
- collection
- picture(*)
(*) picture type is not supported by statistical methods such as entitySelection.max( ).
Optimistic Lock
In "optimistic lock" mode, entities are not locked explicitly before updating them. Each entity has an internal stamp that is automatically incremented each time the entity is saved on disk. The entity.save( ) or entity.drop( ) methods will return an error if the stamp of the loaded entity (in memory) and the stamp of the entity on disk do not match, or if the entity has been dropped. Optimistic locking is only available in ORDA implementation. See also "Pessimistic lock".
Pessimistic Lock
A "pessimistic lock" means that an entity is locked prior to its being accessed, using the entity.lock( ) method. Other processes can neither update nor drop the entity until it is unlocked. The classic 4D language only allows pessimistic locks. See "Optimistic lock".
Privilege
The ability to run one or more actions on resources. Several privileges can be gathered in a role according to the business logic.
Property
See Attribute.
Attributes and properties are similar concepts. "Attribute" is used to designate dataclass properties that store data, while "property" is more generic and defines a piece of data stored within an object.
PropertyPath
A propertyPath is the path to a property in a given object. If the property is nested in several levels, each level separated is by a dot (".").
Regular class
User class not related to an ORDA object.
Related dataclass
These are dataclasses linked by relation attributes.
Relation attribute
Relation attributes are used to conceptualize relations between dataclasses (many-to-one and one-to-many).
- Many-to-one relation (dataclassA references an occurrence of dataclassB): a relation attribute is available in dataclassA and references one instance of dataclassB.
- One-to-many relation (an occurence of dataclassB references several occurrences of dataclassA): a relation attribute is available in dataclassB and references several instances of dataclassA.
A dataclass can have recursive relation attributes.
In an entity, the value of a relation attribute can be an entity or an entity selection.
Related entities
A related entity can be seen as the instance of a relation attribute in a dataclass.
Entity selections may refer to related entities according to the relation attributes defined in the corresponding dataclasses.
Remote datastore
A 4D database opened on a 4D or 4D Server (available through HTTP) and exposed as a REST resource. This database can be referenced locally as a Datastore from other workstations, where it is assigned a locaID. The remote datastore can be used through ORDA concepts (datastore, dataclass, entity selection...). This use is submitted to a licencing system.
Resource
An ORDA element on which any action can be allowed or not according to a privilege. Available resources are: the datastore, a dataclass, a dataclass attribute, an ORDA Data model function, or a project method.
Role
A role is a published privilege intended to be used by an administrator. It can contain one or more privileges.
Session
When the 4D application connects to a Remote datastore, a session is created on the 4D Server (HTTP). A session cookie is generated and associated to the local datastore id.
Each time a new session is opened, a license is used. Each time a session is closed, the license is freed.
Inactive sessions are automatically closed after a timeout. The default timeout is 48 hours, it can be set by the developer (it must be >= 60 minutes).
Shallow copy
A shallow copy only duplicates the structure of elements, and keeps the same internal references. After a shallow copy, two collections will both share the individual elements. See also Deep copy.
Stamp
Used in "optimistic" locking technology. All entities have an internal counter, the stamp, which is incremented each time the entity is saved. By automatically comparing stamps between an entity being saved and its version stored on disk, 4D can prevent concurrent modifications on the same entities.
Storage attribute
A storage attribute (sometimes referred to as a scalar attribute) is the most basic type of attribute in a datastore class and most directly corresponds to a field in a relational database. A storage attribute holds a single value for each entity in the class.