Signal
Sinais são ferramentas fornecidas pela linguagem 4D para gerenciar interações e evitar conflitos entre processos em uma aplicação multiprocesso. Sinais permitem assegurar que um ou mais processos vão esperar por uma tarefa específica a ser completada antes de continuar a execução. Qualquer processo pode esperar ou liberar um sinal.
Os semáforos podem ser usados para gerenciar interações. Os semáforos permitem garantir que dois ou mais processos não modifiquem o mesmo recurso (arquivo, registro...) ao mesmo tempo. Só o processo que estabelece o semáforo pode removê-lo.
Objeto sinal
Um sinal é um objeto partilhado que deve ser passado como parâmetro a comandos que chamam ou criam trabalhadores ou processo.
Um objeto 4D.Signal contém os seguintes métodos e propriedades integrados:
Qualquer worker/processo que chamar o método .wait() suspenderá sua execução até que a propriedade .signaled seja true. Enquanto espera um sinal, o processo que chamar não usa nenhuma CPU. Isso pode ser muito interessante para o rendimento nas aplicações multiprocesso. A propriedade .signaled torna-se true quando qualquer worker/processo chama o método .trigger().
Observe que, para evitar situações de bloqueio, o .wait() também pode retornar depois que um tempo limite definido for atingido.
Os objetos Signal são criados com o comando New signal.
Trabalhar com sinais
Em 4D, você cria um objeto signal chamando o comando New signal. Após criado, esse sinal deve ser passado como parâmetro para os comandos New process ou CALL WORKER para eles poderem modificá-lo quando tiverem concluído a tarefa pela qual você deseja esperar.
- O
signal.wait()deve ser chamado pelo worker/processo que precisa que outro worker/processo termine uma tarefa para poder continuar. - O
signal.trigger()deve ser chamado pelo worker/processo que terminou sua execução para liberar todos os outros.
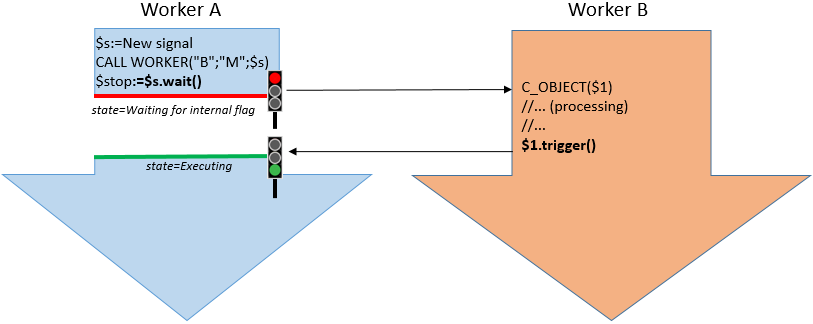
Uma vez que um sinal tenha sido liberado por uma chamada signal.trigger(), ele não poderá ser reutilizado novamente. Se você quiser definir outro sinal, precisará chamar o comando New signal novamente.
Como um objeto de sinal é um objeto compartilhado, você pode usá-lo para retornar resultados de worker/processos chamados, desde que não se esqueça de escrever valores em uma estrutura Use...End use (veja o exemplo).
Exemplo
var $signal : 4D.Signal
// Criação de um sinal
$signal:=New signal
// chamar o processo principal e executar o método OpenForm
CALL WORKER(1;"OpenForm";$signal)
// fazer outro cálculo
...
// Esperando pelo fim do processo
$signaled:=$signal.wait()
// Processamento dos resultados
$calc:=$signal.result+...
Método OpenForm :
#DECLARE ($signal : 4D.Signal)
var $form : Object
$form:=New object("value";0)
// Abrir o formulário
$win:=Open form window("Information";Movable form dialog box)
DIALOG("Information";$form)
CLOSE WINDOW($win)
// Adicione um novo atributo ao seu objeto compartilhado $signal para passar seu resultado ao outro processo:
Use($signal)
$signal.result:=$form.value
End use
// Disparar o sinal para o processo de espera
$signal.trigger()
Resumo
| .description : Text contém uma descrição personalizada para o objeto Signal |
| .signaled : Boolean contém o estado atual do objeto Signal |
| .trigger( ) define a propriedade signaled do objeto de sinal como true |
| .wait( { timeout : Real } ) : Boolean faz com que o processo atual aguarde até que a propriedade .signaled do objeto signal se torne true ou o timeout opcional expire |
.description
História
| Release | Mudanças |
|---|---|
| 17 R4 | Adicionado |
.description : Text
Descrição
A propriedade contém uma descrição personalizada para o objeto Signal.
.description pode ser definida ao criar o objeto signal ou a qualquer momento. Note que uma vez que o objeto Signal é um objeto compartilhado, qualquer acesso ao modo de escrita à propriedade .description deve estar cercado por uma estrutura Use...End use.
Essa propriedade é leitura-escrita.
.signaled
História
| Release | Mudanças |
|---|---|
| 17 R4 | Adicionado |
.signaled : Boolean
Descrição
A propriedade .signaled contém o estado atual do objeto Signal. Quando o sinal é criado, .signaled é False. Torna-se True quando o .trigger( ) é chamado no objeto.
Essa propriedade é somente leitura.
.trigger()
História
| Release | Mudanças |
|---|---|
| 17 R4 | Adicionado |
.trigger( )
| Parâmetro | Tipo | Descrição | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Não exige nenhum parâmetro |
Descrição
A função .trigger( ) define a propriedade signaled do objeto de sinal como true e desperta todos os workers ou processos esperando por este sinal.
Se o sinal já estiver no estado de sinalização (ou seja, a propriedade signaled já for true), a função não faz nada.
.wait()
História
| Release | Mudanças |
|---|---|
| 17 R4 | Adicionado |
.wait( { timeout : Real } ) : Boolean
| Parâmetro | Tipo | Descrição | |
|---|---|---|---|
| timeout | Real | -> | Tempo máximo de espera em segundos |
| Resultados | Parâmetros | <- | Estado da propriedade .signaled |
Descrição
A função .wait( ) faz com que o processo atual aguarde até que a propriedade .signaled do objeto signal se torne true ou o timeout opcional expire.
Para evitar o bloqueio de código, você pode passar um tempo máximo de espera em segundos no parâmetro timeout. Aceitam-se números decimais.
Se o sinal já estiver no estado de sinalização (ou seja, a propriedade .signaled já é true), a função devolve imediatamente, sem esperar.
A função devolve o valor da propriedade .signaled:
- true se o sinal foi acionado (
.trigger()foi chamado). - false se o tempo limite expirou antes de o sinal ser acionado.
Não é recomendável chamar .wait() sem um timeout no processo principal, pois isso pode congelar toda a aplicação 4D.
O estado de um processo que espera um signal é
Waiting for internal flag.