Estrutura
This page displays all of the tables and fields that are exposed as REST resources in the 4D database, including relation attributes (based upon many-to-one and one-to-many relations). In fact, the page displays a view similar to ORDA's datastore.
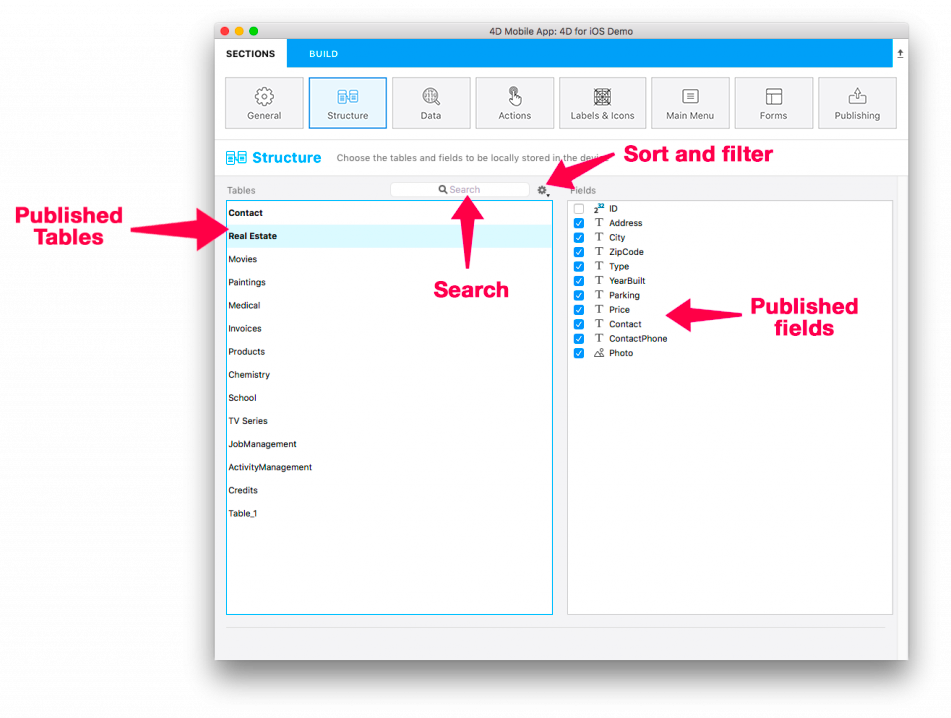
Use this page to define a subset of your physical structure to replicate for mobile devices by selecting the specific tables and fields to publish.
- Published tables will be automatically added as tabs of your app.
- Published scalar fields will be available when defining your list and detail forms.
- Published relation fields (many-to-one and one-to-many) will be available when defining your list and detail forms and come with additional navigation features such as a Relation button.
:::nota
The following tables and fields are not listed in this page:
- tables and fields that do not comply with ORDA rules.
- tables and fields whose name start with "
__" (double underscore).
:::
:::nota
Only computed attributes with values that change over time - only depending on other attributes of the same DataClass - will be updated on the mobile app.
:::
Selecting tables and fields to publish
A table is published when at least one of its fields is published. When a table is published, it is displayed in bold.
To select a field to publish, click on a table name then click on the field in the rightmost list. You can also:
- press the spacebar to select/unselect a field
- use Ctrl+click to select all fields
- use Publish and Publish all from the Fields list local menu.
Filtering lists
When a list has the focus, you can filter its contents using the Search area and a local menu:
- Search area: enter the characters to search within table or field names
- Sort by table name/Sort by field name: sort the list by name. By default, lists are sorted by creation date
- Only published tables/Only published fields: show only tables or fields that have been selected (published)
Supported field types
The mobile editor automatically displays the list of fields that are eligible to the mobile app, depending on their type:
- All 4D scalar field types except BLOB.
- Object fields
- Computed attributes
- Alias attributes returning scalar values (displayed in italics).
- Relation attributes (Many-to-one and One-to-many) are supported and can be selected just as fields. They have specific icons:
- Many to one relation icon:
- One to many relation icon:
- Many to one relation icon:
The names are based upon the relation names in the 4D Structure editor, see the ORDA Structure mapping page.
Using relations
One to Many relations
You can include One to Many relations in your projects and display a list of related fields in a new page of your app.
All you have to do is:
- publishing at least one field of the target (Many) table
- publishing the relation from the source (One) table
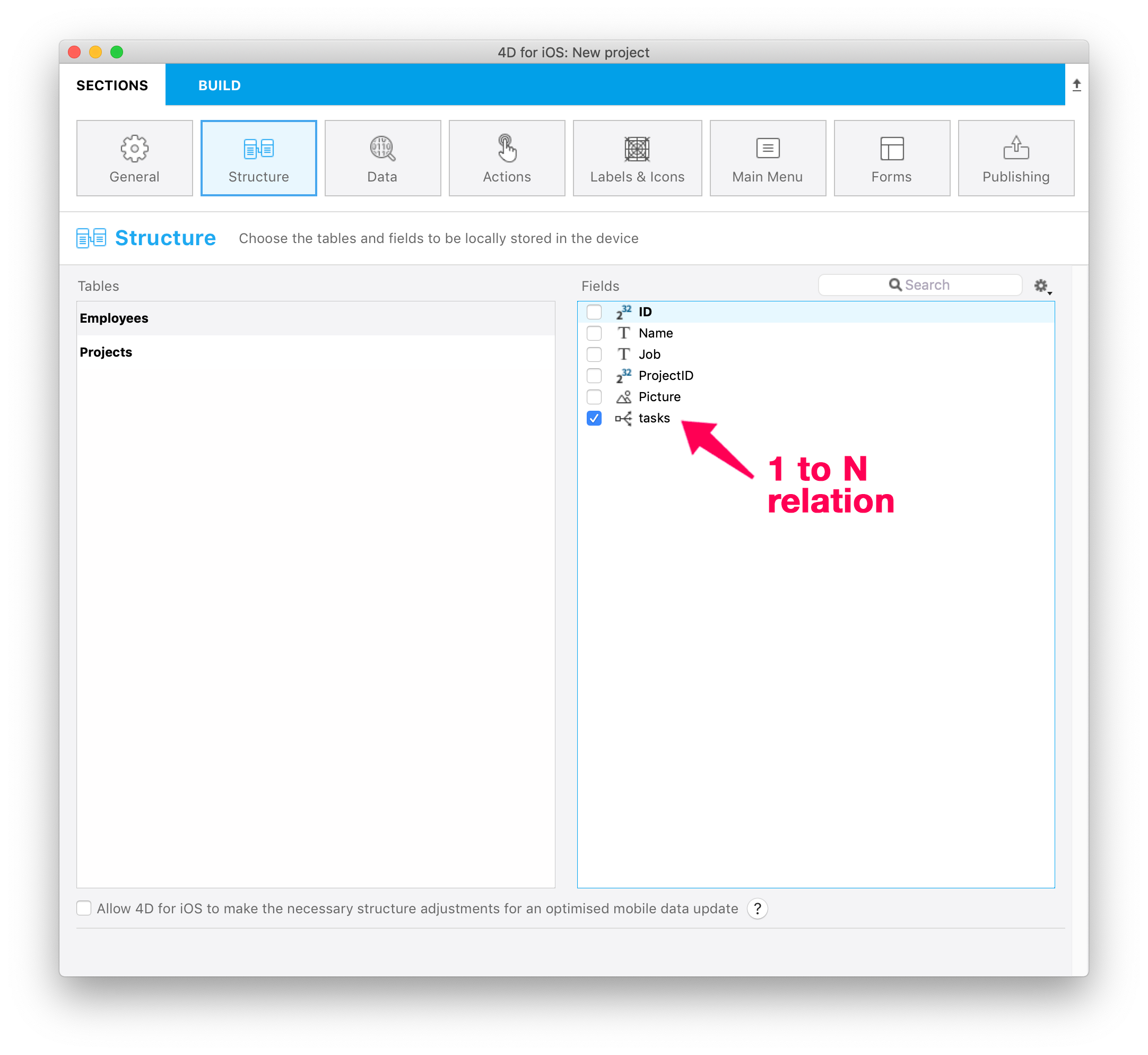
Then, when your related fields are published, they can be used like any other field. So you will be able to:
- Define relations properties in the Labels and Icons page.
- Drop the One to Many relation in a Detail form from the Forms page to create a link between a detail form and a related table. A Relation button will be automatically created in detail forms to go straight to the related view.
See the One to Many relations tutorial for a detailed example of One to Many relation integration in a mobile project.
Many to One relations
Many to one relations can be used like any other field in the app creation process. When you select a Many to One relation in the field list, you can to select which field(s) from the related table to publish in your app:
You just need to click on the relation name, then select the field(s):
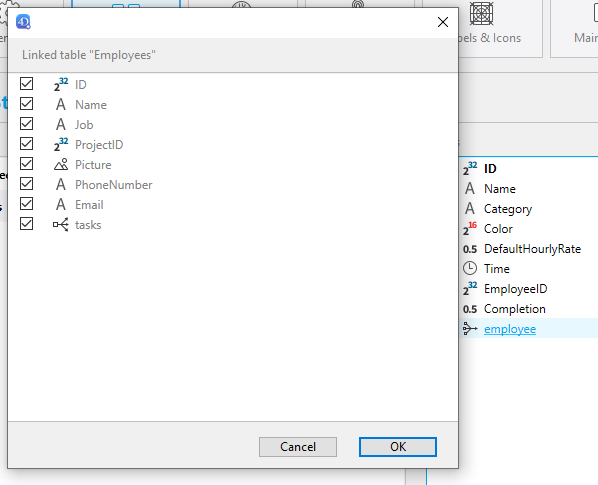
By default, all eligible fields of the related table are published.
See the Many to One relations tutorial for a detailed example of Many to One relation integration in a mobile project.
Many to Many relations
Using the Structure page, you can publish Many to One and One to Many relations from your parent Many to One relations. It means that you can display Many to Many relations in your app and move directly from a List form to another List form.
See the Relation interactions for a detailed example of Many to One relation integration in a mobile project.
Computed attributes
Whether you're working on Android or iOS, you can display computed attributes in your app once it is generated, by configurating them from the project editor. Computed attributes are the result of several fields combined into one field. You will then be able to use this computed attribute as any other field in your mobile app creation process, which means that you will visualize and publish it from the Structure section.
In mobile projects, only scalar computed attributes are supported (i.e. computed attributes where the get function returns a scalar value (text, boolean, date, time, number)).
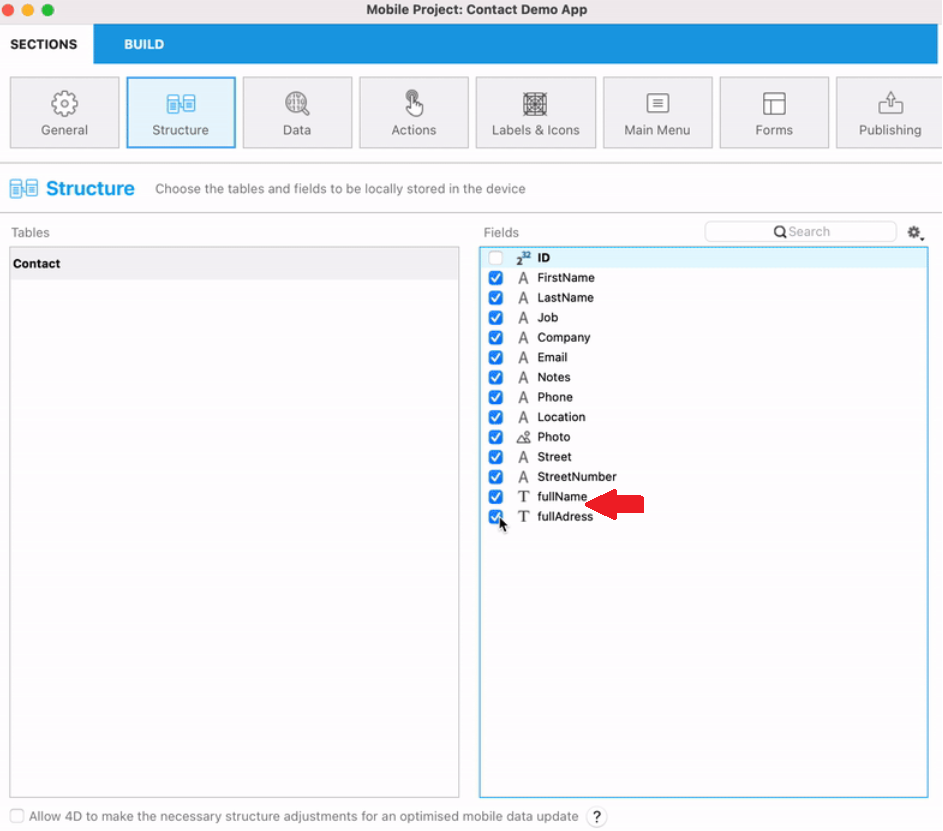
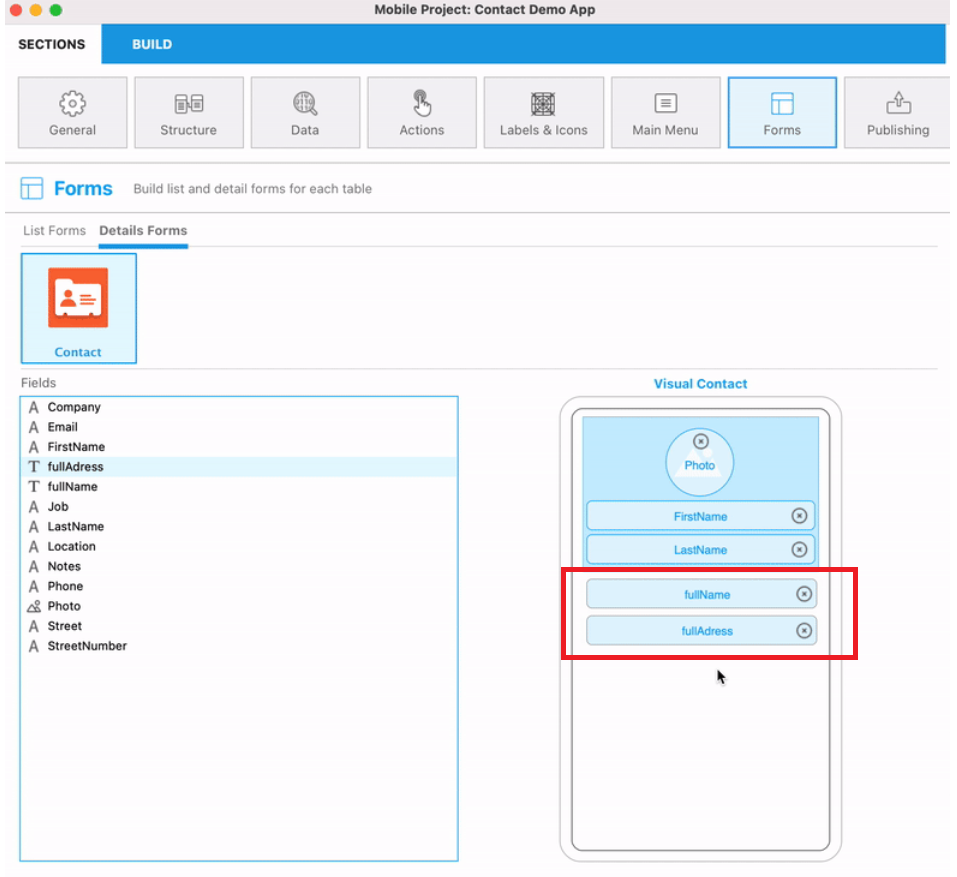
For instance, instead of having two splitted attributes such as the street number and the street name, or the first name and the last name, you can gather both of them in a single attribute that you can name "fullAddress" and "fullName".
The process is actually quite simple!
4D Side
In your code, specify the attributes you want to use and the computed attribute you want to get, using the Class extends and exposed Function syntax, as follows:
Class extends Entity
exposed Function get fullName->$fullName : Text
$fullName:=This.FirstName+" "+This.LastName
exposed Function set fullName($fullName : Text)
$splitName:=Split string($fullName; "/")
If ($splitName.length=2)
This.FirstName:=$splitName[0]
This.LastName:=$splitName[1]
Else
// ERROR
End if
exposed Function get fullAddress->$fullAddress : Text
$fullAddress:=This.StreetNumber+" "+This.Street+" - "+This.Location
exposed Function set fullAddress($fullAddress : Text)
$splitAddress:=Split string($fullAddress; "/")
If ($splitAddress.length=3)
This.StreetNumber:=$splitAddress[0]
This.Street:=$splitAddress[1]
This.Location:=$splitAddress[2]
Else
// ERROR
End if
Project editor side
In the project editor, once the code is written, your computed attributes become available, ready to be published and used as any other field in the creation process:
In the Structure panel:
The exposed computed attributes are displayed in the list of attributes of a dataclass.
In the Label & Icons panel (Icons/short and long labels/formats):
![]()
In the Forms panel:
The computed attributes present in the data model are, like the fields, available in the list of fields of the Forms panel (list and detail). They behave in the same way as the storage attributes of the datastore.
In the Data panel, computed attributes are displayed in the list linked to the "Fields" button of the query filter box.
- Computed attributes can be used with Sort actions.
- A computed attribute without a setter (readOnly) is not available for an Add or Edit action.
- When Add or Edit presets actions are created (if the setter is available and if 4D allows it), computed attributes parameters shall be available when linked to a field.
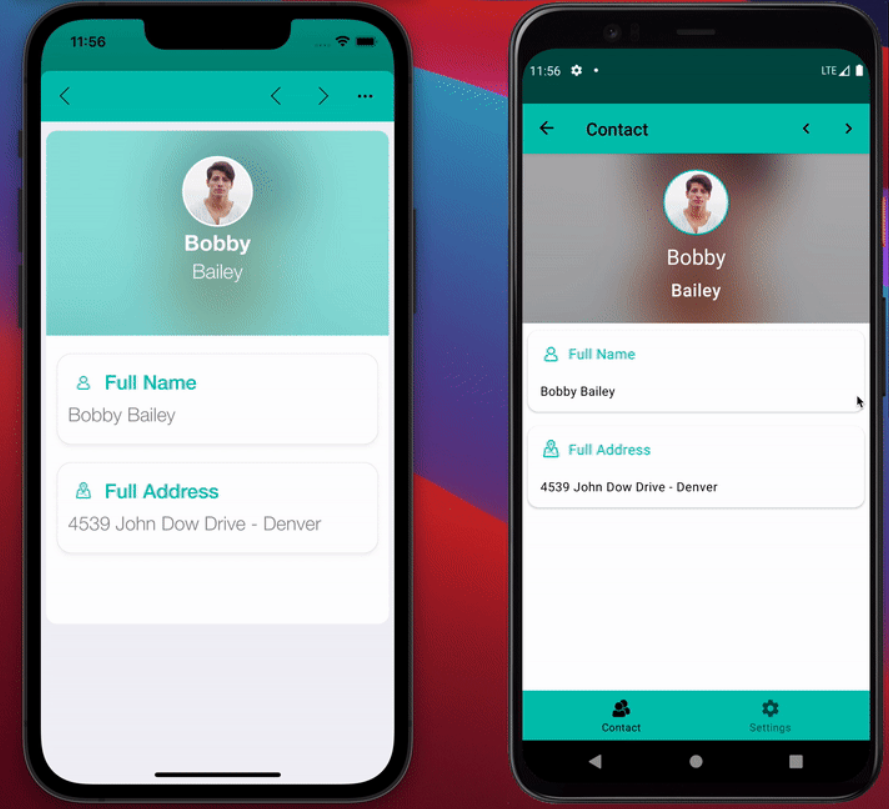
Mobile app side
In the generated mobile application, on iOS or Android, both single attributes and computed attributes are displayed.
Alias attributes
On Android or iOS, you can use scalar alias attributes in your mobile app. An alias attribute is built above another attribute of the data model, named target attribute. The target attribute can belong to a related dataclass (available through any number of relation levels) or to the same dataclass. An alias attribute stores no data, but the path to its target attribute.
Alias attibutes must be exposed to be available to the editor. They are displayed in italics.
In mobile projects, only scalar alias attributes are supported, which means that the kind of the last element of the target attribute path must be "storage". Other kinds are not supported.
Scalar alias attributes can be:
- selected and published like standard fields in the structure editor,
- used to filter data,
- linked to fields as parameters for add and edit preset actions,
- used as any other fields in the Label & Icons section,
- dropped and displayed in forms.
Scalar alias attributes cannot be used as parameters for sort actions.
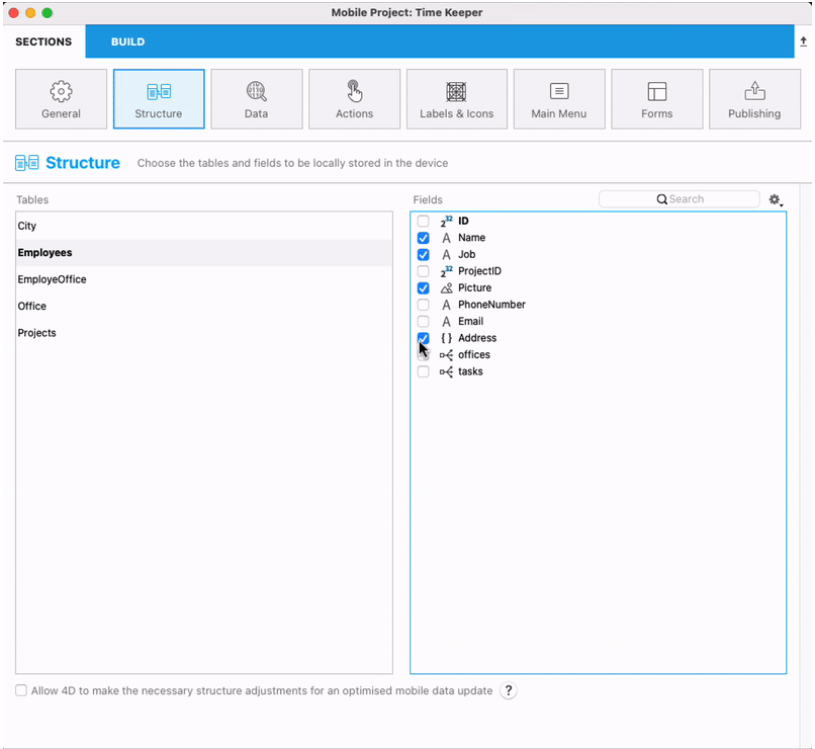
Object attributes
From the Structure section, you can select, use and display all types of attributes in your mobile projects (text, dates, time, integers, etc), including object attributes (JSON format). In the field list, object attributes are distinguished by their {} icon.
You can use an object attribute as any other field in the other sections of the project editor (Data, labels & icons, Forms, etc. except for the Actions section).
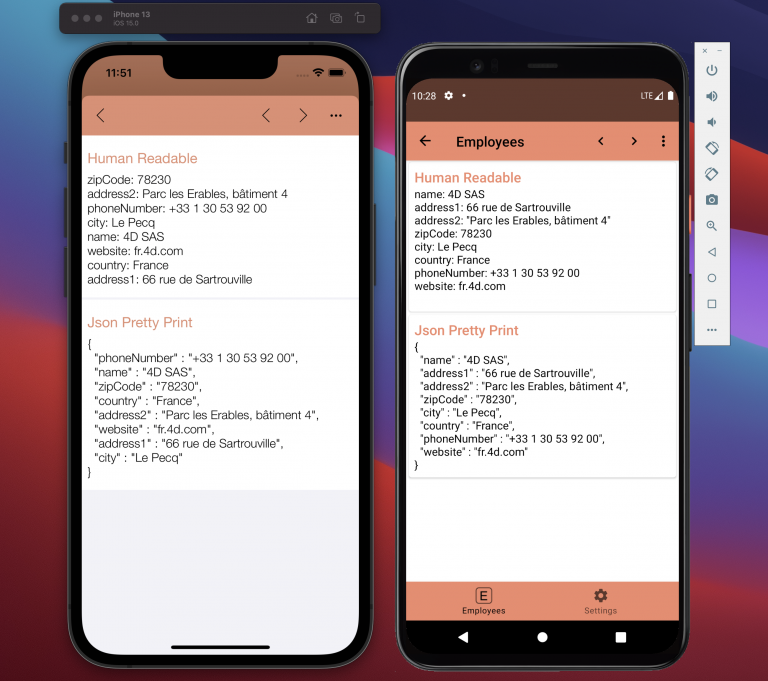
From the Labels&Icons section, two formats are available to display your object attributes:
- Human-readable (YAML): the default format that displays a human-readable structured data in the mobile app
- JSON Pretty Print: the format that displays an indented JSON in the mobile app
![]()
Here's the result on the generated app:
Filter queries
You can use filter queries specific to object attributes in order to return and display filtered data. To do so, simply insert your attribute and property in the Filter query of the Data section.
For instance, consider a Clients table with an Address object-type attribute containing several objects with the following key/values:
{
$Obj:=New object
$Obj.name:="4D SAS"
$Obj.address1:="66 rue de Sartrouville"
$Obj.address2:="Parc les Erables, bâtiment 4"
$Obj.zipCode:="78230"
$Obj.city:="Le Pecq"
$Obj.country:="France"
$Obj.phoneNumber:={
"OfficePhone":"+33 1 30 53 92 00"
"HomePhone":"+33 1 30 53 92 00"
}
$Obj.email:=[
"john@test.com"
"john@4d.com"
]
$Obj.website:="fr.4d.com"
}
Filter by a simple object's value
If you want to display data filtered by an object, such as a list of your clients only based in France, you need to filter your query by country to get only the records containing the France value. Therefore, insert the following syntax in the Filter query field:
Address.country = "France"
Filter by a collection's value
If you want to display data filtered by an element of a collection, such as a specific client's email contained in a collection, you need to filter your query by email to get only the records containing the john@4d.com value. Therefore, insert the following syntax in the Filter query field:
Address.email[] = "john@4d.com"
Incremental reload
Allow structure adjustments
For the best user experience, 4D for iOS and 4D for Android implement an automatic feature for the incremental reload of data. It means that only new, modified or deleted data from the database will be updated to the app. This optimization enhances drastically loading time.
To enable this optimization, 4D for iOS and 4D for Android need the following structure elements:
- A
__DeletedRecordstable to store deleted records - and
__GlobalStampfields to store modification stamps for each published table in your mobile application
You can let the 4D mobile editor do all the work for you and add the necessary structure elements: just select Allow 4D to make necessary structure adjustments for an optimized mobile data update option.
:::nota
These optimizations are required for both local and server databases.
:::
Pull to refresh
On the mobile app side, your data is updated each time you launch your app and each time your app goes foreground, to get constant updated data.
In normal use, simply swipe down from any listform to reload your data.
From iPhone settings, you can reset your app data and find information about your app.
:::nota
When an important maintenance operation is performed on the database side (Recover by tag / Restoration / Compacting) a Full reload is necessary on the mobile app. In this case, the admin shall notify mobile app users.
:::